

Typically, a fire tube boiler can produce up to 4 pounds (5 kg) of steam per hour.Ī water tube is called a boiler, the water through which the water flows through the boiler tube into the steam and the heat flowing through its exterior. In this type of boiler, the thermal field is less because of the flame flow through the drum or tube. The inner tubes of this boiler are usually attached horizontally, vertically, inclined and so on. Namely:įire-tube boilers: A fire tube is called a fire tube boiler, which burns through a boiler’s tube or tube and turns water vapor through its exterior.įire tube boilers are drums or tubes. The boiler can be divided into two main types due to the difference of water or fire heat flow between the boiler tubes. Depending on the production capacity and the number of units of a steam power plant, one or more boilers are installed.
#Steam power generator
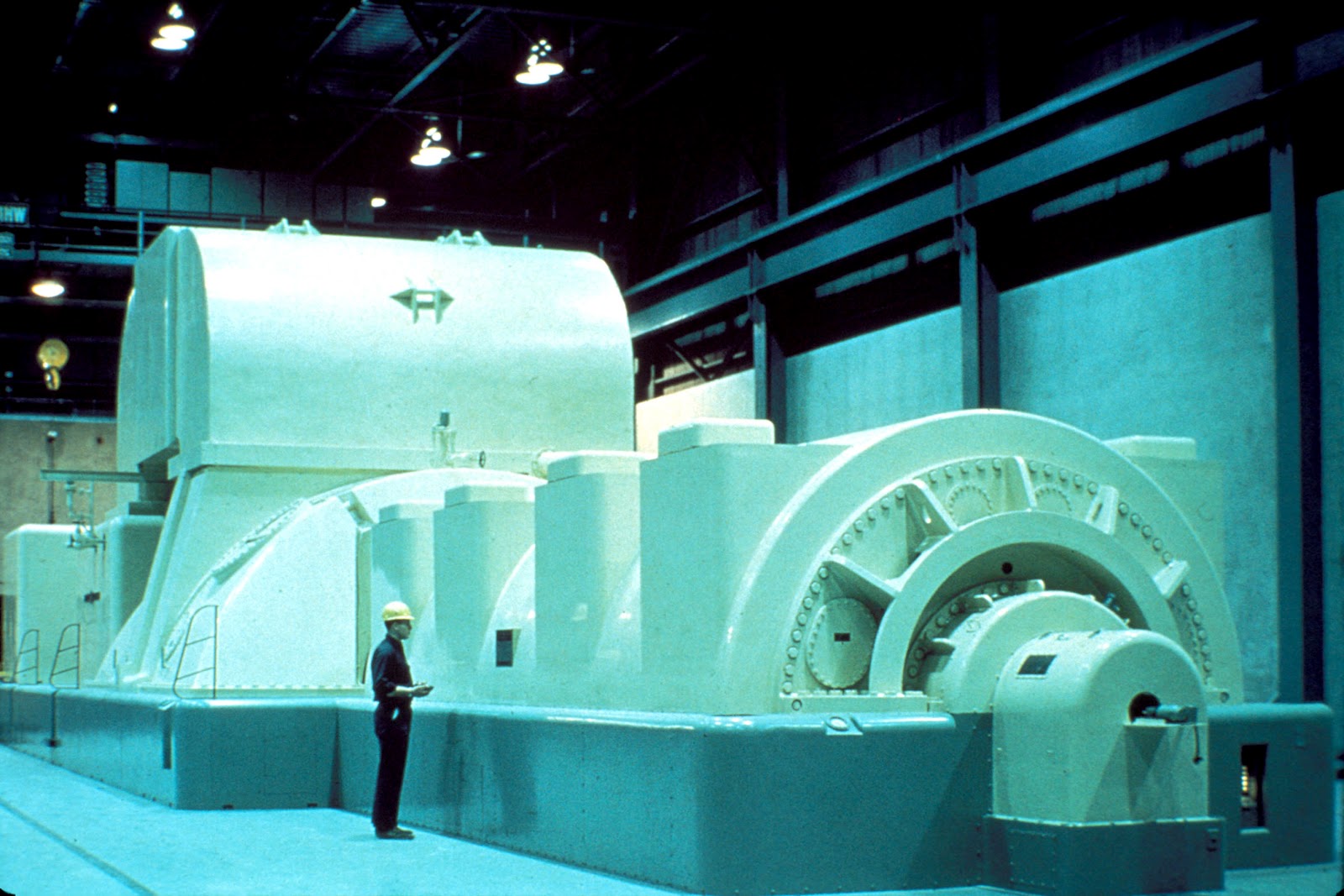
At this steam push, the steam turbine rotation speeds up and generates electrical power from the electric generator, driving the electric generator connected to the shaft of the turbine. The function of the boiler at the steam power station is to convert water into steam in the heat of fuel. The boiler is called a steam generator or steam generator. The following equipment of steam power plant is described below: This section is composed of the following equipment. Oil and gas wells in the United States.This is a very important part of the steam power plant. Some low-temperature resources can be harnessed to generateĮlectricity using binary cycle technology. Low-temperature and co-produced geothermal resources are typically found at temperatures Low-Temperature and Co-Produced Resources Generating capacity in the United States. or about half of the current installed electric power Geological Survey estimates that potentially 500,000 megawatts of EGS resource That are otherwise not economical due to lack of water, location, or rock type. To generate electricity: enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) and low-temperature orĮGS provide geothermal power by tapping into the Earth's deep geothermal resources Whole process, so there are little or no air emissions.Ĭurrently, two types of geothermal resources can be used in binary cycle power plants The water and the working fluid are kept separated during the Heat exchanger and used to turn a turbine. Binary cycle plants use the heat from the hot water to boil a working fluid, usuallyĪn organic compound with a low boiling point. The steam is then separated from the water and used to power a turbine/generator.Īny leftover water and condensed steam are injected back into the reservoir, makingīinary cycle power plants operate on water at lower temperatures of about 225-360 ☏ (107-182 ☌).

This very hot water flows up through wells in the ground under its own pressure.Īs it flows upward, the pressure decreases and some of the hot water boils into steam. With temperatures greater than 360 ☏ (182 ☌).
Since Yellowstone is protected from development, the only dry steam plants in theįlash steam power plants are the most common and use geothermal reservoirs of water


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
